2025. 5. 24. 17:45ㆍCoding Study/Javascript
1. 프로토타입의 개념 이해
1) 상속과 프로토 타입
상속은 객체지향 프로그래밍의 핵심 개념으로 객체의 프로퍼티 또는 메서드를 다른 객체가 상속받아 그대로 사용
이를 통해 불필요한 중복을 제거 한다.
// 생성자 함수
function Circle(radius) {
this.radius = radius;
this.getArea = function () {
// Math.PI는 원주율을 나타내는 상수다.
return Math.PI * this.radius ** 2;
};
}
// 반지름이 1인 인스턴스 생성
const circle1 = new Circle(1);
// 반지름이 2인 인스턴스 생성
const circle2 = new Circle(2);
// Circle 생성자 함수는 인스턴스를 생성할 때마다 동일한 동작을 하는
// getArea 메서드를 중복 생성하고 모든 인스턴스가 중복 소유한다.
// getArea 메서드는 하나만 생성하여 모든 인스턴스가 공유해서 사용하는 것이 바람직하다.
console.log(circle1.getArea === circle2.getArea); // false
console.log(circle1.getArea()); // 3.141592653589793
console.log(circle2.getArea()); // 12.566370614359172

< 상속을 통해 불필요한 중복 제거 방법 >
// 생성자 함수
function Circle(radius) {
this.radius = radius;
}
// Circle 생성자 함수가 생성한 모든 인스턴스가 getArea 메서드를
// 공유해서 사용할 수 있도록 프로토타입에 추가한다.
// 프로토타입은 Circle 생성자 함수의 prototype 프로퍼티에 바인딩되어 있다.
Circle.prototype.getArea = function () {
return Math.PI * this.radius ** 2;
};
// 인스턴스 생성
const circle1 = new Circle(1);
const circle2 = new Circle(2);
// Circle 생성자 함수가 생성한 모든 인스턴스는 부모 객체의 역할을 하는
// 프로토타입 Circle.prototype으로부터 getArea 메서드를 상속받는다.
// 즉, Circle 생성자 함수가 생성하는 모든 인스턴스는 하나의 getArea 메서드를 공유한다.
console.log(circle1.getArea === circle2.getArea); // true
console.log(circle1.getArea()); // 3.141592653589793
console.log(circle2.getArea()); // 12.566370614359172

2) constructor, prototype, instance

new 연산자로 Constructor 를 호출하면 instance 가 만들어 지는데, 이 instance 의 생략 가능한 프로퍼티인 __proto__는
Constructor 의 prototype 을 참조한다.
생성자 함수의 prototype에 어떤 매서드나 프로퍼티가 있다면 인스턴스에서도 마치 자신의 것처럼 사용할 수 있다.
let Person = function (name) {
this._name = name;
};
Person.prototype.getName = function () {
return this._name;
};
let person = new Person("John");
console.log(person.__proto__.getName()); // undfined
console.log(person.getName()); // John
< __proto__ 와 Prototype 의 관계 >
배열 리터럴과 Arry 의 관계
let arr = [1, 2];
console.dir(arr);
console.dir(Array);
첫번째 출력 결과는 arr변수를 출력한 결과
- 생성자 함수 Arry를 원형으로 삼아서 생성되었다는 것을 알 수 있다.
- length 가 2이다.
- 인덱스의 값이 1, 2 이다.
- __proto__를 열어보면 배열에서 사용가능한 메서드 들이 있다.

arr의 __proto__ ([[Prototype]] , 와 Arry 의 prototype 의 매서드가 동일하게 들어 있다.
두번째 출력 결과는 생성자 함수 Arry 를 출력 한 결과이다.
- 함수라는 의미의 f 가 표시되어 있다.
- Arry 함수의 정적메서드 from , isArry ... 등등 이 있다.
- Prototpye 의 내용에는 arr 변수의 __proto__ 와 동일한 내용이 들어가 있다.

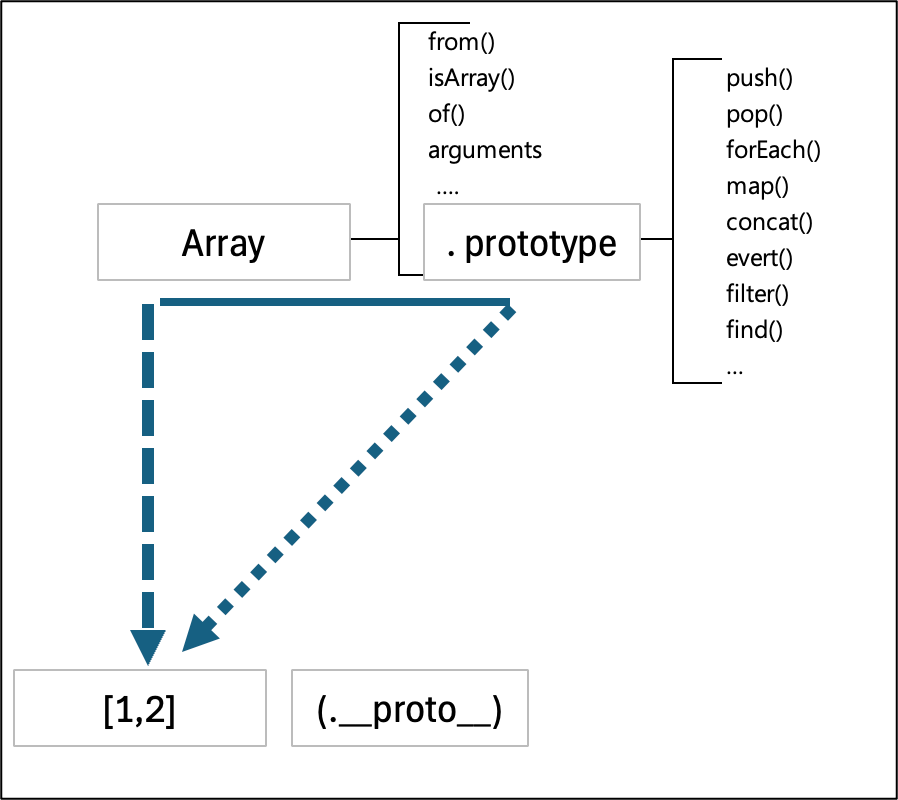
Array 를 new 연산자로 호출해서 생성하든 그냥 배열 리터럴로 생성하든 instance [1,2]가 만들어진다.
이 이스턴스의 __proto__ 는 Array.protorype 을 참조 한다.
__proto__는 생략 가능 하도록 설계 되어 있기 때문에 push, pop, forEach 같은 메서드를 자신의 것 처럼 호출 할 수 있다.
Array prototype 프로퍼티 내부에 있지 않은 매서드는 인스턴스가 호출 할 수 없다.
3) Constructor 프로퍼티
prototype 내부에는 constructor 라는 프로퍼티 가 있다.
인스턴스의 __proto__는 prototype 을 가리키기 때문에 동일하게 가지고 있다.
이 constructor 프로퍼티는 원래의 생성자 함수를 참조한다.
const arr = [1, 2];
console.log(Array.prototype.constructor === Array); //true
console.log(arr.__proto__.constructor === Array); //true
console.log(arr.constructor === Array);//true

계속 해서 참조에 참조로 순환된다.
console.log(
arr.__proto__.constructor.prototype.constructor.prototype.constructor === Array
); //true
< Constructor 변경 >
Constructor 변경 시 참조하는 대상만 변경 될 뿐 이미 만들어진 인스턴스의 원형이 바뀌지는 않는다.
const Person = function (name) {
this._name = name;
};
Person.prototype.getName = function () {
return this._name;
};
let person1 = new Person("John");
console.log(person1.__proto__.getName()); //undefined
console.log(person1.getName()); //John
function NewConstructor() {
this.name = "John";
}
person1.constructor = NewConstructor;
console.log(person1.constructor.name); //NewConstructor
console.log(person1 instanceof NewConstructor); //false person1 의 프로토타입 체인이 아니다.
console.log(person1 instanceof Person); //true person1 의 프로토타입 체인에 있다*instanceof 연산자 : 우변의 생성자 함수가 좌변의 프로토타입 체인상에 존재하면 true를 반환
< constructor 접근방법>
constructor 접근 방법에는 여러가지가 있다.
const Person = function(name) {
this.name = name;
};
let p1 = new Person('사람1'); // Person { name: "사람1" } true
let p1Proto = Object.getPrototypeOf(p1);
let p2 = new Person.prototype.constructor('사람2'); // Person { name: "사람2" } true
let p3 = new p1Proto.constructor('사람3'); // Person { name: "사람3" } true
let p4 = new p1.__proto__.constructor('사람4'); // Person { name: "사람4" } true
let p5 = new p1.constructor('사람5'); // Person { name: "사람5" } true
[p1, p2, p3, p4, p5].forEach(function (p) {
console.log(p, p instanceof Person);
});*getPrototpyeOf(obj) obj 의 prototype 을 반환한다.
< 참고 그림 circle2 를 p로 대체 >

2. 프로토타입 체인
1) 메서드 오버라이드
const Person = (function () {
// 생성자 함수
function Person(name) {
this.name = name;
}
// 프로토타입 메서드
Person.prototype.sayHello = function () {
console.log(`Hi! My name is ${this.name}`);
};
// 생성자 함수를 반환
return Person;
}());
const me = new Person('Lee');
// 인스턴스 메서드
me.sayHello = function () {
console.log(`Hey! My name is ${this.name}`);
};
// 인스턴스 메서드가 호출된다. 프로토타입 메서드는 인스턴스 메서드에 의해 가려진다.
me.sayHello(); // Hey! My name is Lee
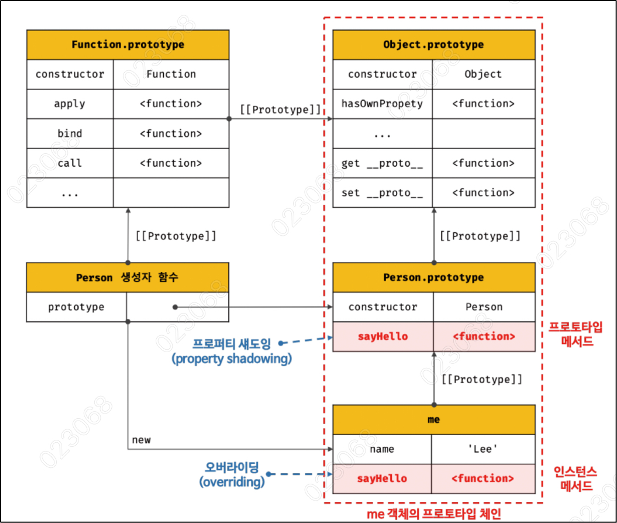
프로토 타입이 소유한 프로퍼티를 프로토타입 프로퍼티
인스턴스가 소유한 프로퍼티를 인스턴스 프로퍼티
프로토 타입 프로퍼티와 같은 이름의 프로퍼티를 인스턴스에서 추가하면 덮어쓰는 것이 아니라 인스턴스 프로퍼티로 추가한다.
이상태에서 prototype 에 있는 메서드에 접근 하게 되면 undefined 가 된다.
console.log(me.__proto__.name); // undefined
하지만 프로퍼티를 지정하면 그 값을 출력 할 수 있다.
Person.prototype.name = "Kim";
me.__proto__.sayHello(); // Hi! My name is Kim
2) 프로토 타입 체인
console.log({ a : 1 });
객체의 내부구조를 출려해서 보게 되면 __proto__ 내부에 또 __proto__가 들어있는 것을 볼 수 있다.

이 트리구조를 그림과 같이 표현해 보면 아래와 같이 볼 수 있다.
이 결과의 의미는 만약 객체가 메서드를 호출 하게 된다면 자신의 프로퍼티를 먼저 검색하고 없으면, 상위 프로토타입의 메서드를
검색하고 그래도 없으면 그 위의 프로토타입의 메서드를 검색해서 있으면 그 메서드를 실행한다.

'Coding Study > Javascript' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 배열 (0) | 2025.08.29 |
|---|---|
| 클래스 (2) | 2025.06.02 |
| 콜백 함수 (0) | 2025.05.10 |
| 실행 컨택스트 (0) | 2025.04.23 |
| 자바스크립트 var, let, const 키워드 (0) | 2025.04.18 |